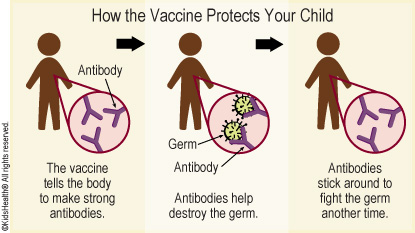
The COVID-19 vaccine can protect your child from getting infected with the coronavirus that causes COVID-19. The vaccine causes the body to create antibodies (special proteins) against the virus. In the future, if your child comes into contact with someone who has the virus, these antibodies will fight the germ and prevent your child from getting sick or make the symptoms milder.
Follow your healthcare provider's recommendations about the timing of vaccine doses and any booster shots.


Your child:

Your child has chest pain, has trouble breathing, or is feeling like their heart is beating too fast, fluttering, or pounding. These symptoms can be a sign of a very rare side effect from the COVID-19 vaccine, called myocarditis. Someone with myocarditis has a swollen heart muscle.
Call 911 if your child has signs of a serious allergic reaction. These include a hoarse voice, wheezing, trouble breathing, a rash, a swollen face, lips, or tongue, looking pale, or feeling very weak or dizzy.

If my child had a COVID-19 vaccine in the past, do they need another one? The virus that causes COVID-19 changes slightly over time. The COVID-19 vaccine is updated to respond to these changes. Getting a COVID-19 vaccine as recommended by your healthcare provider will make sure your child gets the most updated vaccine.
Can the COVID-19 vaccine give my child COVID-19? No, the vaccine can't give a person COVID-19. It contains a small piece of the coronavirus, not the whole virus, so the vaccine can't give people COVID-19.
What are possible side effects from the COVID-19 vaccine? After vaccination, some kids have side effects for 1 or 2 days, such as soreness in the shot area, headache, tiredness, nausea, achiness, or a fever. They can also get swollen glands (lymph nodes) in the armpit or near the collarbone on the side where they got the shot. Very rarely, more serious side effects can happen. Some of these side effects, such as myocarditis, are more likely to happen after a COVID-19 infection than after a vaccination.
Should my child get the COVID-19 vaccine if they've already had COVID-19? Yes, a child can and should get a vaccine even if they have had COVID-19. There are no known risks to getting the vaccine after being infected with coronavirus. We don't know how long a person's immunity lasts after an infection, so it's important to get the vaccine too.