Button batteries are small round batteries that can look like buttons or coins. They're used in hearing aids, toys, watches, calculators, electronic thermometers, key fobs, and remote controls. Swallowing a button battery can cause serious damage to the digestive tract.
Your child swallowed a button battery. Your health care provider gave your child medicine to help them sleep and not feel pain (called anesthesia), then removed the battery. You can now care for your child at home.

Follow your health care provider's instructions for:
Some kids have a sore throat for a few days from the breathing tube used during anesthesia. If your child's throat is sore:

Your child:

Your child:

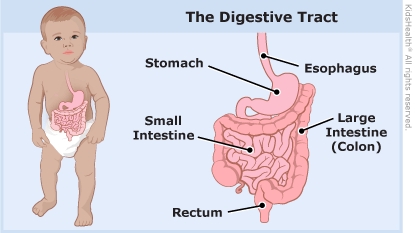
What happens when someone swallows a button battery? When someone swallows a button battery, the electrical charge and leaking chemicals from the battery can damage the digestive tract. Depending on where the battery is in the digestive tract and how long it has been there, it can lead to swelling, blockage, or a breakdown of the digestive tract lining. It can even burn a hole through the digestive tract, which is a serious medical emergency.
How can I protect my child from dangerous items at home? To protect your child:
If your child eats or drinks a dangerous item, call Poison Control right away for advice: 800-222-1222.