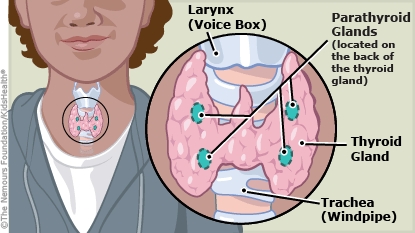
The parathyroids are a group of four small glands in the neck that make parathyroid hormone. A hormone is a chemical messenger that carries instructions to different parts of the body, telling them what to do and when. Parathyroid hormone helps balance the amount of calcium in the blood.
In hypoparathyroidism, the parathyroid glands don't release enough parathyroid hormone, so blood calcium levels become too low. Treatment increases the blood calcium levels and includes medicines, calcium and vitamin D supplements, and changes in the diet. Checking the blood levels of calcium regularly helps healthcare providers keep the calcium at the right level. Sometimes other treatments are needed.
With treatment and good control of the calcium levels, kids with hypoparathyroidism can lead a healthy life.

Follow your healthcare provider's directions for:

Your child has symptoms of hypoparathyroidism, such as:

Your child is having a seizure (has jerking of one or more body parts).

What causes hypoparathyroidism? In kids, hypoparathyroidism can be congenital (meaning they were born with it). It also can be caused by surgery on the parathyroid or thyroid glands, or by a neck injury. In children and teens, hypoparathyroidism can occur when the immune system attacks the parathyroid glands. Sometimes hypoparathyroidism can run in families.
Why is it important to have the right amount of calcium in the blood? The right amount of calcium is needed for bone health and for keeping the muscles, brain, and nervous system working properly. Low calcium in the blood can lead to muscle spasms or cramps, seizures, abnormal heartbeat, and feeling tired, nervous, or sad.
What problems can happen? Over time, people with low calcium can develop cataracts (clouding of the lenses of the eyes), bone and tooth problems, brittle hair and fingernails, and dry skin.