Scabies is a common skin problem that happens when tiny mites burrow into the skin, causing itching and a rash with sores or blisters. Scabies is very contagious. If bacteria get into the blisters, a skin infection can happen. With treatment, scabies usually goes away without any long-lasting problems.

Everyone in the household should be treated, even if they have no signs of scabies.
Usually, health care providers prescribe a cream or lotion to put on the skin to kill the mites, but sometimes they use a medicine to be taken by mouth instead. Follow your health care provider's instructions for using the medicine.
If using a cream or lotion:
If using medicine given by mouth:
Other things to know:

Your child:

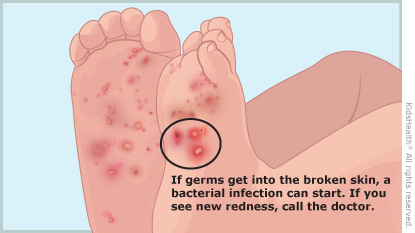
What are the signs of scabies? Scabies mites burrow into the top layer of skin, where they lay their eggs. A person with scabies usually has severe itching, which might be worse at night. A rash with small bumps or blisters develops. Sometimes raised wavy lines where the mites have burrowed may appear, especially on the inner part of the wrist or between the fingers or toes.
How does scabies spread? Scabies spreads easily through skin-to-skin contact. People who get scabies for the first time may not have any symptoms for 4–6 weeks, but they can still spread mites during that time. It's also possible to catch scabies from items like clothes, towels, or bedding. Scabies also can spread by sexual contact.