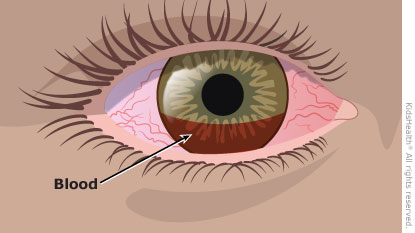
A hyphema is when blood pools in the front part of the eye (called the anterior chamber). In children, it is usually caused by an eye injury; for example, by getting hit by a ball or a fist. Treatment for a hyphema (hi-FEE-muh) includes limiting your child's activity, using eye drops, and having frequent checks by the health care provider.
A hyphema is a serious eye injury that can lead to other problems, including vision loss. Follow these instructions closely to help your child heal.


You have any questions about your child's care.


What are the symptoms of a hyphema? A hyphema can cause eye pain, sensitivity to light, blurred vision, changes in vision or vision loss, nausea, or vomiting (throwing up).
What problems can happen from a hyphema? Sometimes an eye with hyphema can bleed again, especially in the first 5 days after the injury. A hyphema also can lead to glaucoma (increased eye pressure), cataracts (a cloudy lens), damage to the eye nerve, blindness, and other eye problems.
How can we prevent another hyphema? Most eye injuries can be prevented by wearing protective eyewear. Regular glasses do not protect the eyes well. To prevent future eye injuries, your child should: