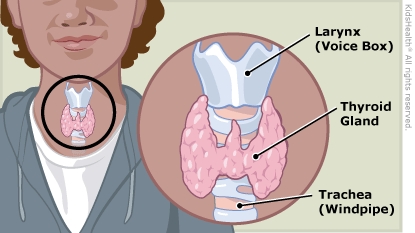
The thyroid makes hormones that do many important things, such as helping with brain development, growth, pubertal development, and how the body uses energy. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is a chronic (ongoing) condition where the body's immune system attacks the thyroid.
Some people with Hashimoto's thyroiditis (also called chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis) have normal thyroid function for a while. But over time, the thyroid stops making enough thyroid hormone. If needed, health care providers prescribe thyroid hormone medicine to bring the body's levels back to normal and help with symptoms.


Your child has:

Your child is very sleepy or confused, or has a seizure.

What are the symptoms of Hashimoto's thyroiditis? Most kids with Hashimoto's thyroiditis have symptoms because their thyroid hormones are low (called hypothyroidism). The most common symptoms are a goiter and not growing well or going through puberty as expected. Other symptoms can include feeling tired and cold, constipation, dry skin, and weight gain.
Less often, kids with Hashimoto's thyroiditis can have too much thyroid hormone (called hyperthyroidism). This can cause weight loss, jitteriness, fast heartbeat, and other symptoms.
How is Hashimoto's thyroiditis treated? Health care providers decide on treatment based on symptoms and blood test results. They usually treat hypothyroidism and goiters with thyroid hormone taken as a pill. Sometimes, they do surgery to treat a goiter, especially if the thyroid gets big enough to cause problems with swallowing.
What causes Hashimoto's thyroiditis? The exact cause is not known. Some people have a genetic (inherited) tendency that makes them more likely to get Hashimoto's thyroiditis.