Your child was in the hospital to get medical care for the coughing, wheezing, and other problems caused by bronchiolitis. You can now care for your child at home. Your child should feel better within a week or so, but the coughing may continue for several weeks.


Your child:

Call 911 if your child is struggling to breathe, is too out of breath to talk or walk, or turns blue.

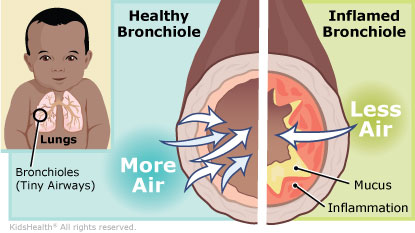
What causes bronchiolitis? Kids get bronchiolitis because a virus — like RSV (respiratory syncytial virus), rhinovirus (the cold virus), or influenza (the flu virus) — gets into their lungs. The viruses can irritate tiny airways called bronchioles. The airways swell and fill with mucus, making kids wheeze.
How is it treated? Most treatments for bronchiolitis are to help kids feel more comfortable while their bodies heal. Antibiotics don't help bronchiolitis because they don't work against viruses.
Can bronchiolitis spread to others? The viruses that cause bronchiolitis can spread from one person to another. Keep your child home from school or child care until there is no fever or runny nose for at least 24 hours.
To help prevent the spread of viruses, all family members should:
Can bronchiolitis cause any long-term problems? Kids who were in the hospital for bronchiolitis as babies may wheeze more often than other kids. But after age 10, their chance of wheezing is about the same as that of other kids.
Can bronchiolitis come back? Because lots of different viruses can cause bronchiolitis, kids may get it more than once — just like a cold or the flu. Hand washing is the best protection against viruses.
If your baby was born early or has a health condition, ask about the RSV shot. It doesn't prevent RSV, but it can make bronchiolitis less severe if a baby does get it.