Gastroesophageal reflux is when food and acid from the stomach go back up into the esophagus, and sometimes out the mouth or nose. Reflux that causes problems like poor growth or damage to the esophagus is called gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Kids with GERD need treatment. Follow these instructions to care for your child.


Your child:


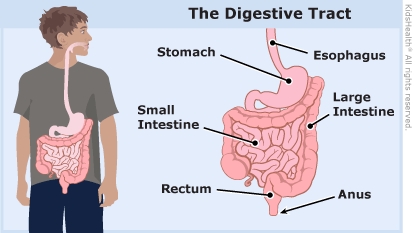
What causes reflux? Reflux happens because a ring of muscle at the bottom of the esophagus (the tube that runs from the mouth to the stomach) does not close all the way. This ring of muscle is called the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). If the LES does not close normally, food and fluid from the stomach can come up the esophagus, into the back of the throat, and sometimes out the mouth or nose.
What are the signs of reflux? Kids with reflux may have no signs. Or they may have pain or burning in the upper chest. They may have the feeling of stomach acid coming up into the back of the throat or have a sour taste in the mouth. Other symptoms of GERD include spitting up or vomiting, stomach pain, and cough.
How is GERD diagnosed? Health care providers diagnose GERD by asking about signs of reflux and checking a child's growth. Usually tests aren't needed to know if a child has GERD.